What is UI/UX Design
User experience and user interface can sound very similar but are very different. This article is a short guide to know details about what is UI/UX design.

Whenever the concept of website design comes up, the terms “user experience (UX)” and “user interface (UI)” come in close continuation. While the concepts of UX and UI have been around for some time, there often is some confusion while differentiating between the two. Let’s explore what is UI/UX design along with the various nuances and differences between these concepts in this blog.
Exploring UI
Imagine a common place where humans and machines can go and interact with each other. That is what the user interface means in a nutshell. A user interface enables you to complete a myriad of tasks or helps towards the completion of a set target. Funnily enough, right at this moment, you are reading this article with the help of a user interface.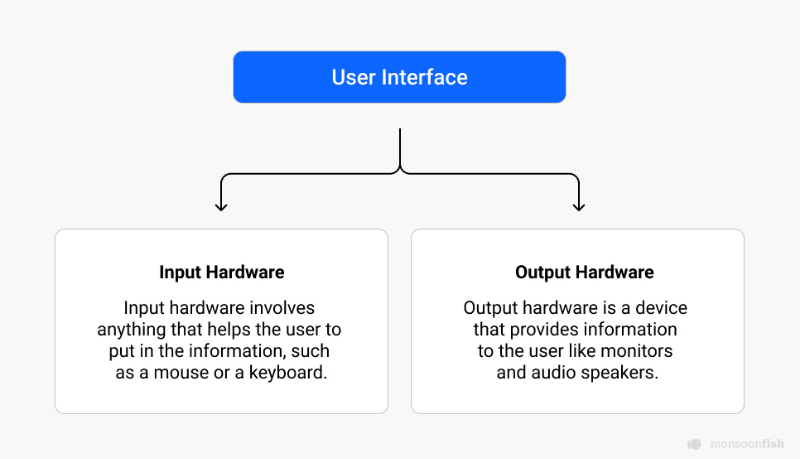
User interfaces can be divided into two primary things: input hardware and output hardware. Input hardware involves anything that helps the user to put in the information, such as a mouse or a keyboard. On the other hand, output hardware is a device that provides information to the user like monitors and audio speakers. When these two modules work together, the user can fully control the device.
There are many different types of user interfaces. The three most common UIs are command-line interface, graphic user interfaces, and voice-enabled user interface.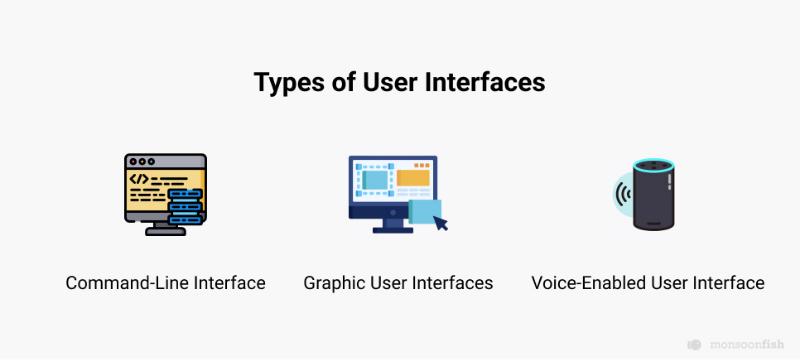
The Characteristics of UI

Any optimally designed UI should possess the following characteristics:
- Clarity
All the elements in a UI should be easily understandable and decodable by the end user. The instructions and utility should be such that it feels organic for the user to walk through it. - Consistency:
There’s always a pattern that users follow when using a product. A brand’s UI should be distinguishable from others. - Efficiency:
When the user input is minimal and the output is maximised, know that the UI is truly efficient. The provision of shortcuts and gestures increases productivity for seasoned users.
An example of this can be found here.
What Does a UI Designer Do?
A UI designer is fundamentally focused on the virtual representation of information. The aesthetics of a design play a vital role in the advancement of any product. UI designers need to possess several skills under their hat, including but not limited to graphic design, visual design, and branding design skills to create interfaces that have an aesthetically pleasing vibe. Imagine dressing up nicely and covering yourself with vivid and vibrant clothes. That’s exactly what these designers do with raw information. They wrap it in a pleasing and vibrant design for the end-users.
Having a keen sense of attention to detail is a must for any UI designer. The tiniest element can have an ever-lasting impact on the user interface. ‘The devil is in the details’ is quite rightly put.
The end goal of every UI design is to solve a problem being faced by the end user. Designers make themselves ready to spend time finding a proper solution to these issues. Users can face a myriad of problems, for which the designers should constantly be prepared to solve.
Exploring UX
In this process, the design team creates products that provide relevant and useful experiences to the users. Because, in the end, it’s all about the users. Branding, design, utility, and functionality are all different aspects of the multifaceted User Experience design.
“No product is an island. A product is more than the product itself. It is a cohesive, integrated set of experiences. Think through all of the stages of a product or service – from initial intentions through final reflections, from the first usage to help, service, and maintenance. Make them all work together seamlessly.”
— Don Norman, inventor of the term “User Experience”
The Characteristics of UX
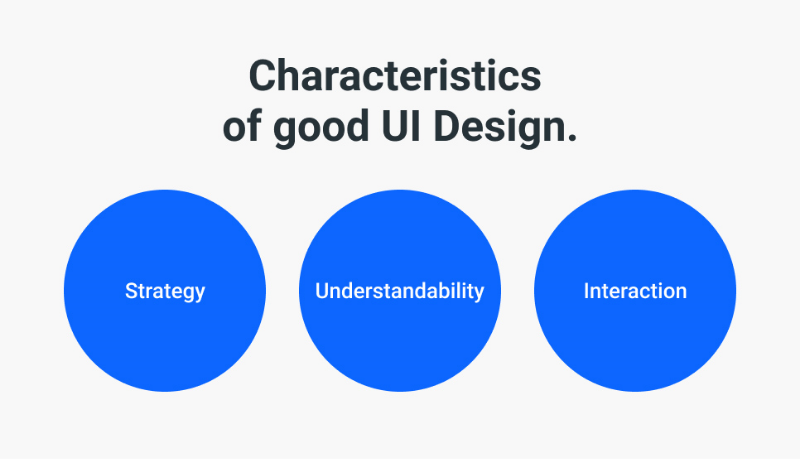
- Understandability
There is profound research conducted to understand and integrate the users’ understandability, their wants, and their needs. Moreover, the research is usually conducted to single out the target audience’s needs and wants. An integral arrow in a designer’s quiver is empathy. With empathy, the designers enable themselves to understand, read, and explore the absolute needs and wants of their target audience. - Strategy
Strategy is the next integral cog in the workings of a UX designer. Having an ironclad plan and strategy to tackle all the purposes of a product is what makes the design useful. Mapping a design is having a journey on its own. - Interaction
UX designers have a keen eye on how the users are using the product, their preferences, and their mode of operation. All insights are used in proposing better design solutions.
What Does a UX Designer Do?
Optimal UX design gives a competitive edge to companies who are in cutthroat competition in the market. These are the companies or brands that understand and are willing to invest in good designs. As a result, the role of a UX designer emerged and is in high demand.
UX design is a progressive way of designing products. Click here to view an example of UX implementation.
Every company desires to know the target audience’s wants and needs. With the help of UX design, a company can intricately learn what the users need and in what quantity. UX design also helps the company curate and create products that meet the customers’ preferences. UX design service is a multidisciplinary field where UX designers can be involved in different areas of product development such as product research, ideation, prototyping, testing.
The Key Skills of a UX/UI Designer

The brief given to UX/UI designer s varies exponentially in accordance with the brand they’re working for. Several professional UX/UI designers have come in from different professions that had transferable talents and skills. Several visual designers, software developers, and digital marketing officials have branched onto UI/UX design.
Coming from a varied range of educational backgrounds, these designers need to garner a lot of technical skills. A degree in graphic design or web design could be another feather on their hat. UI/UX designers need a range of technical skills such as UX research, wireframing and prototyping, interaction design, visual communication, and information architecture.
The perfect UI/UX designer must exhibit several soft skills in addition to their designing prowess. Soft skills have the power to turn an average designer into a pathbreaking one. These soft skills include being optimal at communication, curiosity, and being empathetic to the end-users.
Career Options for UX/UI Designers
Acquiring these particular skills invite a lot of new opportunities for a steady career. Specialisations including UX writing, interaction design, usability testing, visual design, and more are what sum up these job roles. Let’s see what jobs UI/UX designers can pursue:
- UI/UX Design
For this job, one has to collect a database of research insights in order to scope out the users’ needs. For this, designers usually employ the help of wireframing and prototyping, followed by usability tests. Combining UX and UI into a single all-round product is a new trend now. - Visual Design
As the name suggests, these designers are responsible for giving a visually pleasing look to a tangible or digital product. The interface is designed by them. While designing it, they need to work in close proximity with interaction designers and copywriters to build an interface that looks good, is easy to understand and is efficient. They may also assist UI/UX designers with developing high-fidelity prototypes towards the end of the design phase. - Research Roles
Research is a vital element of being a UI/UX designer. They garner information and inputs from the users by conducting interviews, surveys, or basic observation of the users. They also host focus groups stationed in their natural habitat to keep a track of their usage and issues. This role also includes analyzing data for the UI/UX team to further their respective operations. - Coding
These people are human links between the design and engineering teams. They are a bridge of sorts connecting two very different worlds. Their area of focus is to convert a design into reality. A UX engineer’s arsenal includes computer languages such as HTML, JS, CSS, and so on. - Website Design
UX/UI designs have paved the path for several custom elements that are incorporated in websites for a holistic and user-friendly interface. The primary goal behind adding such elements and to understand what is UI/UX design, it is essential to encourage the users to actively engage while on the platform.
Several elements such as animated videos, audio and graphics are being incorporated in a website to uphold the designer’s end of the communication with the users. The success of these sites explains why interactive design has become such an overwhelmingly popular trend in current website design. View more information here.
The Traits of a UX/UI Designer
A UI/UX developer is a multifaceted professional. There are multiple disciplines that a developer needs to maintain if they aim to have a working career as a UI/UX developer.

- Always Put The User First
Walk a mile in the users’ shoes and you’ll understand what needs to change in your design. Implementing these processes based on the research gathered is what developers should always focus on. Empathy is the bread and butter for a developer. A developer needs to pinpoint what makes a user tick. - Being Tech-Savvy
Today, we are surrounded by gadgets and technological advancements. But, these gadgets are only useful when the user knows how to effectively employ them. A UI/UX designer’s job is to create user-friendly interfaces that enable users to understand how to use complex technical products. Having a big hand in the design process, every developer must first understand what the program or product is designed for and only then will they be able to help the end-users. - Problem-solving Skills
Every product or design will have its fair share of problems with it. The users are entitled to feel confused or lost at some point or the other. A UI/UX designer should have all the conscious tools to effectively tackle these situations as and when they arise. Patience and thorough knowledge of designing will help them solve the users’ problems. - Effective Communication
Communicating is an important arrow in a developer’s quiver. This is because the role is so collaborative. You should also be able to discuss design principles with non-design folks, such as developers. Designers often have to host training sessions or present their designs in a hall full of people. These tasks demand high levels of confidence and presentation skills. Presenting a design or product in the best way is half the battle won.
UX and UI have always been interchangeable in the minds of most people. However, it is quite untrue. It’s true that these crafts are very closely connected to one another. But, it is also true that there is a world of differences between them. In a nutshell, UX design is based on the cognitive skills of your brain. These designs play with the analytical side of your brain. On the other hand, UI design services focus on being aesthetically pleasing other than anything else. It plays on the visual side, making it a better and more vivid experience for the users.
It’s always suggested to try walking on both these paths, and then making an informed decision as to which option is more suitable for you. Real-world experience is vital in making such important choices. It’s important to define the type of design that you find most interesting and focus on honing the skills to create outstanding design solutions.
CATEGORIES





